S. Arnaboldi, G. Salinas, S. Bichon, S. Gounel, N. Mano, A. Kuhn
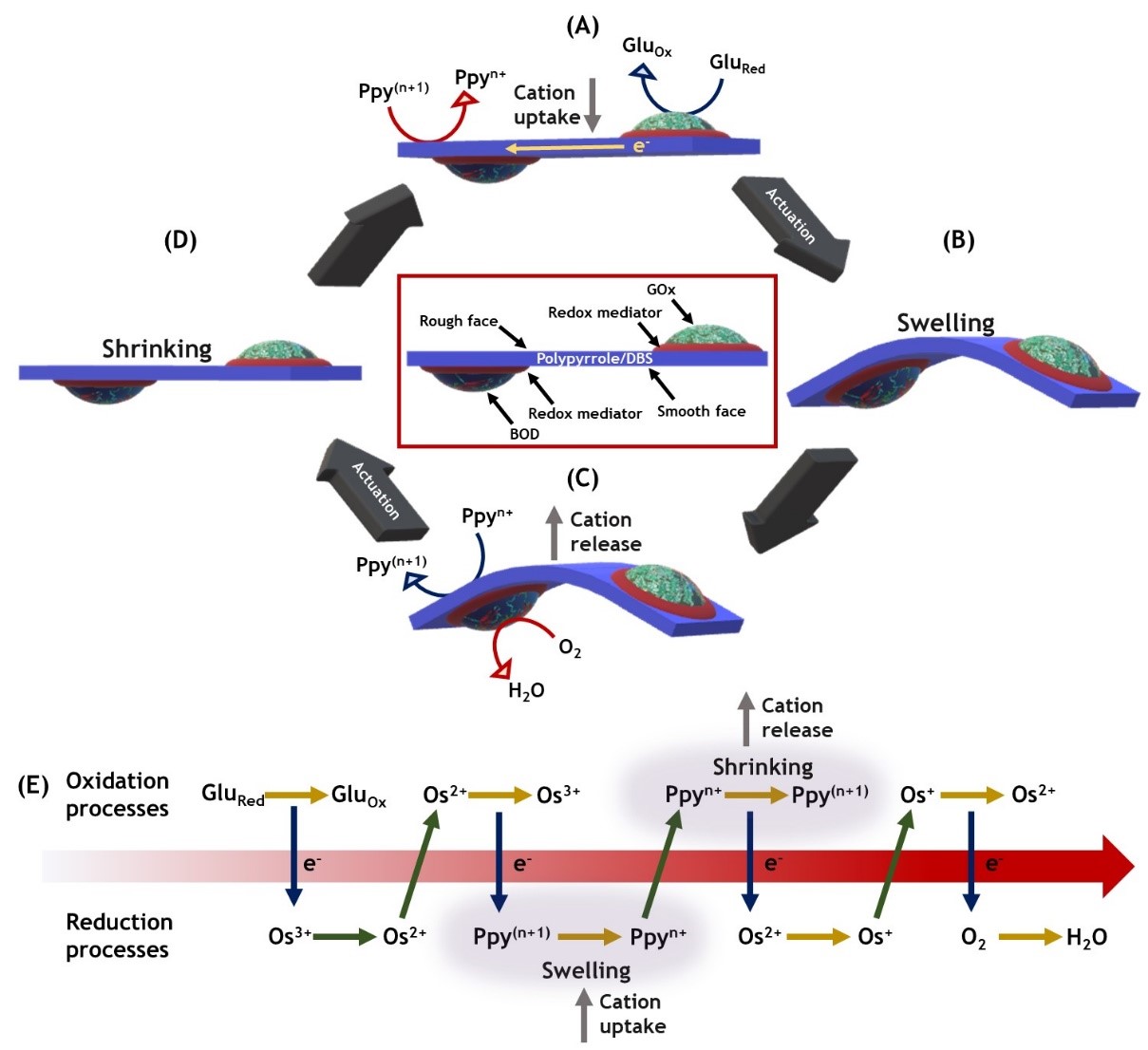
Artificial actuators have been extensively studied due to their wide range of applications from soft robotics to biomedicine. Herein we introduce an autonomous bi-enzymatic system where reversible motion is triggered by the spontaneous oxidation and reduction of glucose and oxygen, respectively. This chemo-mechanical actuation is completely autonomous and does not require any external trigger to induce self-sustained motion. The device takes advantage of the asymmetric uptake and release of ions on the anisotropic surface of a conducting polymer strip, occurring during the operation of the enzymes glucose oxidase and bilirubin oxidase immobilized on its surface. Both enzymes are connected via a redox polymer at each extremity of the strip, but at the opposite faces of the polymer film. The time-asymmetric consumption of both fuels by the enzymatic reactions produces a double break of symmetry of the film, leading to autonomous actuation. An additional break of symmetry, introduced by the irreversible overoxidation of one extremity of the polymer film, leads to a crawling-type motion of the free-standing polymer film. These reactions occur in a virtually unlimited continuous loop, causing long-term autonomous actuation of the device.